Business
Streamlining the road to net-zero through carbon reporting

By Paul Rekhi, Head of Carbon Services at Advantage Utilities
Understanding the evolution of our carbon footprint is key to comprehending the urgency and significance of emission reduction today. According to the Global Carbon Project, between 2011 and 2020, carbon dioxide emissions averaged at 38.8 billion tons per year, but our land and ocean sinks which convert this CO2 have only been able to support 21.7 billion tons yearly. This deficit in emissions is what has caused the atmospheric CO2 growth rate which in turn has led to global warming and climate change. These are defining issues for businesses, hence the need to report and then reduce carbon emissions is more important than ever. I recently hosted a webinar where I discussed this very point, advising businesses on how to implement a credible plan to achieve net-zero as well as lower energy costs.
In this article, I will share those insights, discussing how ESG emerged as a key consideration for businesses today. I will then outline how businesses can go about measuring their carbon by using the carbon-ethics cycle which includes the steps they should take to streamline the road to net-zero via effective carbon reporting.

The distinction between net-zero and carbon neutral
There is an important distinction to be made about what we mean by ‘net-zero’ and ‘carbon neutral’. Net-zero involves counting emissions, then organically removing these emissions from the business. What carbon neutrality involves is the same accounting principle of greenhouse gas (GHG) accounting but also taking accredited carbon offsets to help counteract GHGs released and reaching a zero-carbon footprint. However, to get to true net-zero you have to account for it – that means having oversight into your scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions.
Scope 1 emissions are direct emissions such as company facilities and vehicles. Scope 2 emissions primarily involve indirect emissions stemming from purchased electricity, heating and cooling. Finally, Scope 3 emissions involve everything else your business does; this starts with upstream activities, everything that happens before your organisation – ‘from cradle to gate’, including bought goods, employee commuting and leased assets, through to downstream activities, everything that happens after – from gate to grave, such as processing of solid products, transportation and investments.
The importance of carbon reporting
As corporate guidance emerged and the damaging effects of excess carbon emissions were accepted, this led to large companies being required to report on their scope 1 and 2 emissions. If an organisation meets two or more of the following criteria; a turnover or gross income of £36 million or more; balance sheet assets of £18 million or more; or 250 employees or more; then they must stay compliant with UK government regulations such as theStreamlined Energy and Carbon Reporting (SECR) and Energy Savings Opportunity Scheme (ESOS). Of the 5.5 million UK businesses, only 7,000 fall into the category of having over 250 employees.
But this is not just a checkbox exercise, it is a strategic move. Proper carbon reporting not only ensures compliance but also positions your organisation as a responsible and forward-thinking entity, which is why it has become widely accepted for organisations to establish an ESG department.
The carbon-ethics cycle
To enable businesses to track their carbon emissions, we created our carbon-ethics cycle, to enable organisations to measure, manage and reduce their emissions as efficiently as possible.
Our starting point is to understand businesses – their sites, their objectives and their needs. From here, businesses should measure and certify their scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions which act as an organisation’s benchmark on how much carbon was associated with their business, within a given period – usually by financial year. Without first measuring emissions, you cannot manage emissions, making progress towards net-zero very difficult.
Once we have that benchmark, consultation with each department of the business is crucial to effectively reducing emissions, looking at how energy is used (when and where) as well as how it is procured. From there, technology such as solar PV, heat pumps and voltage optimisation, can be used to make energy savings and increase sustainability.
Reducing/offsetting emissions may also be necessary if reducing emissions is not possible. The final step is to report and re-certify their emissions, allowing comparisons to be made to benchmark data. And this is an ongoing process, so the cycle can begin again on the journey to net-zero. But what this cycle achieves is a streamlined process that enables the most progress to take place.
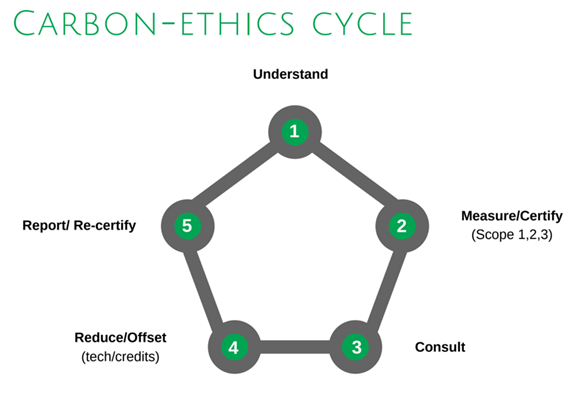
So where are we right now? With large companies required to report on their carbon, other companies are also taking it upon themselves to expand their own reporting. There are several types of clients that get in touch with us to measure their carbon and reduce their emissions. One of them are the large companies, but others include organisations with supply chain partners requesting carbon data, companies with competitors measuring carbon emissions, environmentally conscious companies as well as others.
A structure to measuring carbon within your organisation
Businesses all start from the same position: having to change their processes and behaviour in order to measure carbon. Progress is only made by building upon this foundation, with Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) offering the next step in ensuring compliance throughout the business. On top of that, policies are overlaid which runs and controls the business.
But there are also two ‘floors’ that are missing in this structure. The first of these is accounting, reporting and marketing. Without measuring and accounting what it is that you are doing as a business, the effects of your progress will be minimal, which is why marketing is also crucial to enhancing brand image and customer loyalty. The final step is planning and execution, fundamental to realising your organisation’s goals. This cannot be forgotten as this is where businesses must ensure they have all the experience, expertise, knowledge and skills in place to report for what they do.
To conclude, businesses implementing carbon reporting will find that progress towards net-zero is far easier. The need to reduce emissions is clear and the systematic measurement, management, and subsequent reduction of emissions is made a tangible possibility through the streamlined and efficient approach outlined in the carbon-ethics cycle. A collaborative and structured carbon reporting process allows businesses to meet reduction targets successfully, ultimately leading to the attainment of net-zero status.
You may like
Business
How 5G and AI shaping the future of eHealth

Global Director for AI/ML Solutions, Mona Nia Tecnotree
The digital transformation of the healthcare industry continues to gain momentum. This shift can be attributed to the rapid advancement of widely applied technologies such as 5G networks, cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and big data.
Moreover, integrating 5G networks with cloud-based healthcare platforms and AI is driving the emergence of intelligent eHealth technology, projected to reach $208 billion by 2030, according to recent reports. Recent research by Grand View Research emphasises that the synergy between 5G and AI is pivotal in transforming healthcare by enabling faster data exchange, reducing latency, and improving the reliability of health solutions. This collaboration aims to revolutionise the healthcare sector by facilitating hyper-personalisation, optimised care, enhanced sales and services, and streamlined operations. Leading venture firms actively invest in healthcare start-ups using AI, fostering a rapidly growing ecosystem of innovative advancements.
As AI and 5G continue to make waves through all industries, healthcare needs to adapt to changes quickly. However, with operational, security, and data privacy concerns, healthcare organisations remain wary. As such, they must analyse their current and future needs to understand how AI and 5G technologies can help fulfil them and establish a comprehensive plan to guarantee its efficient and secure implementation in their practices.
Recent research by the International Data Corporation (IDC) emphasises that the synergy between 5G and AI could potentially reduce operational costs by up to 20% and improve patient outcomes by enabling more accurate diagnostics and personalised treatments.
5G Integration in eHealth
5G technology stands at the forefront of healthcare reform with its superior data speed and dramatically reduced latency. Tailored to concurrently accommodate multiple connected devices such as sensors, wearables and medical equipment, 5G is truly indispensable in healthcare, allowing IoT devices to seamlessly transmit accurate data for healthcare providers.
It empowers healthcare professionals to handle large, high-definition files like clinical visuals, videos, and real-time patient insights. 5G’s capability for network slicing—dedicating specific network segments for certain uses—simplifies the management of such files. In addition, it optimises the performance of each application, thereby removing the strain on medical staff.
However, the implementation of 5G technology shouldn’t be oversimplified. It’s essential to analyse the potential risks and challenges thoroughly. A principal component to consider is regulatory cybersecurity and data privacy. Given that 5G networks are susceptible to cyber attacks, it falls upon healthcare providers to protect data such as patient information.
Organisations should also consider the financial implications of implementing 5G technology, as it involves a considerable investment in infrastructure and equipment. Therefore, they must balance the potential gains against the costs to ensure the viability of the investment.
Recent discussions at Mobile World Congress 2024 highlighted the critical role of regulatory frameworks in ensuring the secure deployment of 5G in healthcare. Experts advocated for robust cybersecurity measures and collaborative efforts between technology providers and healthcare institutions to mitigate potential risks.
Marrying 5G and AI for Improved eHealth Solutions
Despite the challenges, integrating 5G and AI will pave the way for unprecedented growth within the internal medical ecosystem, enhancing healthcare quality and patient results. For example, deploying data to carry out descriptive-predictive-prescriptive analytics and transmitting the acquired insights using 5G can drastically improve the user experience while helping make informed decisions. Such an approach can assist healthcare organisations in identifying promising healthcare use cases like remote patient monitoring, surgical robotics, and telemedicine.
Moreover, AI-facilitated hyper-personalisation, driven by the profusion of data accessible through 5G networks, can evaluate patient histories, genetic profiles, and lifestyle elements alongside real-time vitals to prescribe tailored advice and treatments. AI can also automate scheduling appointments, streamline supply chain management, and enhance transactions such as claims and prior authorisations. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can deliver real-life support, while patient and customer service applications can provide an enriched experience through increased data accessibility.
AI can also streamline healthcare services by predicting and managing disease outbreaks. Supported by 5G’s capacity for real-time operability, AI systems can instantly analyse patient data, oversee bed availability, and notify medical personnel of potential complications—promoting efficient, effective care delivery.
Finally, AI-empowered fraud detection algorithms operating on 5G networks can analyse copious amounts of data in real time to detect suspicious activities and alert responsible security teams. This can also be applied to security cameras that can detect anomalies in patients’ and visitors’ behaviour and notify appropriate staff members.
A study published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (JMIR) in 2023 demonstrated that combining AI and 5G in telemedicine significantly improved patient satisfaction and reduced consultation times by 30%.
Shaping an AI Blueprint for 5G eHealth
Integrating AI and 5G technologies can revolutionise disease assessment and surveillance, facilitating more precise diagnostics and tailored treatments. In return, it will drastically improve the standard of care, curbing expenses and boosting efficiency.
Over the next few years, healthcare providers should focus on specific areas where 5G and AI can deliver the most impact. For example, developing telehealth platforms that excel in security, accessibility, and user-friendly interfaces will be paramount. This design aspect is set to thrive, particularly with 5G paving the way for high-definition video consultations, remote patient monitoring, and instant data sharing between patients and healthcare
providers.
The precision and availability of diagnostic applications powered by AI and tele diagnostic services will notably increase in tandem with the widespread adoption of 5G. The strategic emphasis should be on enriching its capabilities, ensuring compatibility with existing systems, and seamlessly integrating the tech into existing healthcare processes.
AI-guided care management systems will also play an integral role in eHealth. There is a need to structure these systems to constantly monitor patient progress, suggest highly personalised treatments, and coordinate care across multiple providers while prioritising patient privacy and data protection.
Finally, when it comes to home health monitoring, emphasis should be placed on creating IoT devices that can integrate seamlessly with AI-driven health platforms and securely transmit data; this will be a critical development within the field.
The synergy between 5G technology and AI will continue revolutionising the healthcare industry, offering more customised, efficient, and cost-friendly solutions. By developing a precise AI blueprint for critical eHealth applications and capitalising on the capabilities of 5G, the benefits will drastically outweigh the challenges.
Business
Driving business success in today’s data-driven world through data governance

Source: Finance derivative
Andrew Abraham, Global Managing Director, Data Quality, Experian
It’s a well-known fact that we are living through a period of digital transformation, where new technology is revolutionising how we live, learn, and work. However, what this has also led to is a significant increase in data. This data holds immense value, yet many businesses across all sectors struggle to manage it effectively. They often face challenges such as fragmented data silos or lack the expertise and resources to leverage their datasets to the fullest.
As a result, data governance has become an essential topic for executives and industry leaders. In a data-driven world, its importance cannot be overstated. Combine that with governments and regulatory bodies rightly stepping up oversight of the digital world to protect citizens’ private and personal data. This has resulted in businesses also having to comply e with several statutes more accurately and frequently.
We recently conducted some research to gauge businesses’ attitudes toward data governance in today’s economy. The findings are not surprising: 83% of those surveyed acknowledged that data governance should no longer be an afterthought and could give them a strategic advantage. This is especially true for gaining a competitive edge, improving service delivery, and ensuring robust compliance and security measures.
However, the research also showed that businesses face inherent obstacles, including difficulties in integration and scalability and poor data quality, when it comes to managing data effectively and responsibly throughout its lifecycle.
So, what are the three fundamental steps to ensure effective data governance?
Regularly reviewing Data Governance approaches and policies
Understanding your whole data estate, having clarity about who owns the data, and implementing rules to govern its use means being able to assess whether you can operate efficiently and identify where to drive operational improvements. To do that effectively, you need the right data governance framework. Implementing a robust data governance framework will allow businesses to ensure their data is fit for purpose, improves accuracy, and mitigates the detrimental impact of data silos.
The research also found that data governance approaches are typically reviewed annually (46%), with another 47% reviewing it more frequently. Whilst the specific timeframe differs for each business, they should review policies more frequently than annually. Interestingly, 6% of companies surveyed in our research have it under continual review.
Assembling the right team
A strong team is crucial for effective cross-departmental data governance.
The research identified that almost three-quarters of organisations, particularly in the healthcare industry, are managing data governance in-house. Nearly half of the businesses surveyed had already established dedicated data governance teams to oversee daily operations and mitigate potential security risks.
This strategic investment highlights the proactive approach to enhancing data practices to achieve a competitive edge and improve their financial performance. The emphasis on organisational focus highlights the pivotal role of dedicated teams in upholding data integrity and compliance standards.
Choose data governance investments wisely
With AI changing how businesses are run and being seen as a critical differentiator, nearly three-quarters of our research said data governance is the cornerstone to better AI. Why? Effective data governance is essential for optimising AI capabilities, improving data quality, automated access control, metadata management, data security, and integration.
In addition, almost every business surveyed said it will invest in its data governance approaches in the next two years. This includes investing in high-quality technologies and tools and improving data literacy and skills internally.
Regarding automation, the research showed that under half currently use automated tools or technologies for data governance; 48% are exploring options, and 15% said they have no plans.
This shows us a clear appetite for data governance investment, particularly in automated tools and new technologies. These investments also reflect a proactive stance in adapting to technological changes and ensuring robust data management practices that support innovation and sustainable growth.
Looking ahead
Ultimately, the research showed that 86% of businesses recognised the growing importance of data governance over the next five years. This indicates that effective data governance will only increase its importance in navigating digital transformation and regulatory demands.
This means businesses must address challenges like integrating governance into operations, improving data quality, ensuring scalability, and keeping pace with evolving technology to mitigate risks such as compliance failures, security breaches, and data integrity issues.
Embracing automation will also streamline data governance processes, allowing organisations to enhance compliance, strengthen security measures, and boost operational efficiency. By investing strategically in these areas, businesses can gain a competitive advantage, thrive in a data-driven landscape, and effectively manage emerging risks.
Auto
The Benefits of EV Salary Sacrifice: A Guide for Employers and Employees

As the UK government continues to push for greener initiatives, electric cars have become increasingly popular. The main attraction for both employers and employees is the EV salary sacrifice scheme.
By participating in an EV salary sacrifice scheme, both employers and employees can enjoy cost savings and contribute to environmental sustainability along the way! This article will delve into the specifics of how these schemes operate, the financial advantages they offer, and the broader positive impacts on sustainability.
We will provide a comprehensive overview of the mechanics behind EV salary sacrifice schemes and discuss the various ways in which they benefit both employees and employers, ultimately supporting the transition to a greener future in the UK.
What is an EV Salary Sacrifice Scheme?
An EV salary sacrifice scheme is a flexible financial arrangement that permits employees to lease an EV through their employer. The key feature of this scheme is that the leasing cost is deducted directly from the employee’s gross salary before tax and National Insurance contributions are applied. By reducing the taxable income, employees can benefit from substantial savings on both tax and National Insurance payments. This arrangement not only makes EVs more affordable for employees but also aligns with governmental incentives to reduce carbon emissions.
For employers, implementing an EV salary sacrifice scheme can lead to cost efficiencies as well. The reduction in National Insurance contributions on the employee’s reduced gross salary can offset some of the costs associated with administering the scheme. Additionally, such programmes can enhance the overall benefits package offered by the employer, making the company more attractive to prospective and current employees.
Benefits for Employees
1. Tax and National Insurance Savings
By opting for an EV salary sacrifice scheme, employees can benefit from reduced tax and National Insurance contributions. Since the lease payments are made from the gross salary, the taxable income decreases, resulting in substantial savings.
2. Access to Premium EVs
Leading salary sacrifice car schemes often provide access to high-end electric vehicles that might be otherwise unaffordable. Employees can enjoy the latest EV models with advanced features, contributing to a more enjoyable and environmentally friendly driving experience.
3. Lower Running Costs
Electric vehicles typically have lower running costs compared to traditional petrol or diesel cars. With savings on fuel, reduced maintenance costs, and exemptions from certain charges (such as London’s Congestion Charge), employees can enjoy significant long-term financial benefits.
4. Environmental Impact
Driving an electric vehicle reduces the carbon footprint and supports the UK’s goal of achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. Employees can take pride in contributing to a cleaner environment.
Benefits for Employers
1. Attract and Retain Talent
Offering an EV salary sacrifice scheme can enhance an employer’s benefits package, making it more attractive to potential recruits. It also helps in retaining current employees by providing them with valuable and cost-effective benefits.
2. Cost Neutrality
For employers, EV salary sacrifice schemes are often cost-neutral. The savings on National Insurance contributions can offset the administrative costs of running the scheme, making it an economically viable option.
3. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Implementing an EV salary sacrifice scheme demonstrates a commitment to sustainability and corporate social responsibility. This can improve the company’s public image and align with broader environmental goals.
4. Employee Well-being
Providing employees with a cost-effective means to drive electric vehicles can contribute to their overall well-being. With lower running costs and the convenience of driving a new EV, employees may experience reduced financial stress and increased job satisfaction.
How to Implement an EV Salary Sacrifice Scheme
1. Assess Feasibility
Evaluate whether an EV salary sacrifice scheme is feasible for your organisation. Consider the number of interested employees, potential cost savings, and administrative requirements.
2. Choose a Provider
Select a reputable provider that offers a range of electric vehicles and comprehensive support services. Ensure they can handle the administrative tasks and provide a seamless experience for both the employer and employees.
3. Communicate the Benefits
Educate your employees about the advantages of the scheme. Highlight the financial savings, environmental impact, and access to premium EV models. Provide clear guidance on how they can participate in the programme.
4. Monitor and Review
Regularly review the scheme’s performance to ensure it continues to meet the needs of your employees and the organisation. Gather feedback and make adjustments as necessary to enhance the programme’s effectiveness.
Conclusion
The EV salary sacrifice scheme offers a win-win situation for both employers and employees in the UK. With significant financial savings, access to premium vehicles, and a positive environmental impact, it’s an attractive option for forward-thinking organisations. By implementing such a scheme, employers can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and employee well-being, while employees can enjoy the benefits of driving an electric vehicle at a reduced cost.
Adopting an EV salary sacrifice scheme is a step towards a greener, more sustainable future for everyone.

Stealthy Malware: How Does it Work and How Should Enterprises Mitigate It?

How 5G and AI shaping the future of eHealth

Driving business success in today’s data-driven world through data governance

The Sustainability Carrot Could be More Powerful Than the Stick!

Hybrid cloud adoption: why vendors are making the switch in 2022 and why you should too


